MP Board 10th Elimination Method of solving a pair of linear equations : आप “विलोपन विधि” (Elimination Method) सीख रहे हैं और प्रश्नावली 3.4 को हल करना चाहते हैं। यहाँ पहले विलोपन विधि का स्पष्टीकरण और फिर प्रश्नावली 3.4 के सभी प्रश्नों का हल दिया गया है।
3.4.2 विलोपन विधि (Elimination Method)
विलोपन विधि का अर्थ है “एक चर (variable) को विलुप्त करना” या “हटाना”।
यह विधि अक्सर प्रतिस्थापन विधि से अधिक सुविधाजनक होती है। इसका लक्ष्य किसी एक चर (![]() या
या ![]() ) के गुणांकों (coefficients) को दोनों समीकरणों में एक जैसा बनाना है।
) के गुणांकों (coefficients) को दोनों समीकरणों में एक जैसा बनाना है।
उदाहरण (जैसा आपकी किताब में है):
![]() — (1)
— (1)
![]() — (2)
— (2)
- लक्ष्य:
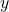 के गुणांकों को समान करना (दोनों को 12 बनाना)।
के गुणांकों को समान करना (दोनों को 12 बनाना)। - गुणा: समीकरण (1) को 3 से और समीकरण (2) को 4 से गुणा करें।
 — (3)
— (3) — (4)
— (4)
- विलोपन: अब
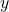 के गुणांक (
के गुणांक (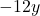 ) समान हैं। हम समीकरण (4) में से (3) को घटाकर
) समान हैं। हम समीकरण (4) में से (3) को घटाकर 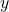 को विलुप्त कर सकते हैं।
को विलुप्त कर सकते हैं।
- हल:
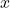 का मान किसी भी समीकरण (जैसे 1) में रखकर
का मान किसी भी समीकरण (जैसे 1) में रखकर 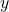 ज्ञात कर लें।
ज्ञात कर लें।
प्रश्नावली 3.4 के हल
1. निम्न समीकरणों के युग्म को विलोपन विधि तथा प्रतिस्थापन विधि से हल कीजिए:
(i) 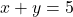 और
और 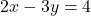
- (a) विलोपन विधि (Elimination):
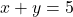 — (1)
— (1)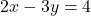 — (2)समीकरण (1) को 3 से गुणा करने पर:
— (2)समीकरण (1) को 3 से गुणा करने पर: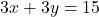 — (3)समीकरण (2) और (3) को जोड़ने पर:
— (3)समीकरण (2) और (3) को जोड़ने पर:
का मान (1) में रखने पर:![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com (2x - 3y) + (3x + 3y) = 4 + 15<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1e6ef2c38c4eaebe48042874c18a57e2_l3.png" height="19" width="182" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[5x = 19 \implies \mathbf{x = 19/5}\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>x](https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c870585587cc0f912fdc3cdd83280824_l3.png)
का मान![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com (19/5) + y = 5<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-50ea169ff7f4fa777a7e8e093722e460_l3.png" height="73" width="582" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[y = 5 - (19/5) = (25-19)/5 \implies \mathbf{y = 6/5}$</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --> <!-- wp:list-item --> <li>(b) प्रतिस्थापन विधि (Substitution):समीकरण (1) से: $x = 5 - y$इसे (2) में रखने पर: $2(5 - y) - 3y = 4\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>10 - 2y - 3y = 4<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f3707b6af9f00f66dfcfab4f4dd13670_l3.png" height="19" width="189" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[-5y = -6 \implies \mathbf{y = 6/5}\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>y](https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8c65ed0d12c0bf0e47c46f0f5c5096b5_l3.png)
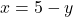 में रखने पर:
में रखने पर:
- हल:
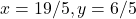
- कौन-सी विधि अधिक उपयुक्त है? विलोपन विधि (
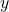 के गुणांकों को बराबर करना) यहाँ थोड़ी तेज है।
के गुणांकों को बराबर करना) यहाँ थोड़ी तेज है।
(ii) 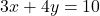 और
और 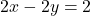
- (a) विलोपन विधि (Elimination):
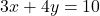 — (1)
— (1)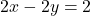 — (2)समीकरण (2) को 2 से गुणा करने पर:
— (2)समीकरण (2) को 2 से गुणा करने पर: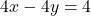 — (3)समीकरण (1) और (3) को जोड़ने पर:
— (3)समीकरण (1) और (3) को जोड़ने पर:
का मान (1) में रखने पर:![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com (3x + 4y) + (4x - 4y) = 10 + 4<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9f34e2b5199cf8cc356142bf618c4375_l3.png" height="14" width="153" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[7x = 14 \implies \mathbf{x = 2}\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>x](https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9c662b35f37258ea87daba312719b2eb_l3.png)
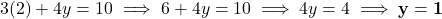
- (b) प्रतिस्थापन विधि (Substitution):समीकरण (2) से:
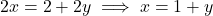 इसे (1) में रखने पर:
इसे (1) में रखने पर: *** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula: 3(1 + y) + 4y = 10<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-efed48720b2563045cb9ed771ce734b9_l3.png" height="16" width="130" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[3 + 3y + 4y = 10\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>7y = 7 \implies \mathbf{y = 1}<pre class="ql-errors">*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula: \[y$ का मान $x = 1 + y$ में रखने पर:$x = 1 + 1 \implies \mathbf{x = 2}$</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --> <!-- wp:list-item --> <li><strong>हल:</strong> $x = 2, y = 1$</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --> <!-- wp:list-item --> <li><strong>कौन-सी विधि अधिक उपयुक्त है?</strong> दोनों ही विधियाँ यहाँ बहुत आसान हैं।</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --></ul> <!-- /wp:list --> <!-- wp:separator --> <hr class="wp-block-separator has-alpha-channel-opacity"/> <!-- /wp:separator --> <!-- wp:heading {"level":4} --> <h4 class="wp-block-heading">(iii) $3x - 5y - 4 = 0$ और $9x = 2y + 7$</h4> <!-- /wp:heading --> <!-- wp:paragraph --> पहले समीकरणों को मानक रूप में लिखें: <!-- /wp:paragraph --> <!-- wp:paragraph --> $3x - 5y = 4$ --- (1) <!-- /wp:paragraph --> <!-- wp:paragraph --> $9x - 2y = 7$ --- (2) <!-- /wp:paragraph --> <!-- wp:list --> <ul class="wp-block-list"><!-- wp:list-item --> <li>(a) विलोपन विधि (Elimination):समीकरण (1) को 3 से गुणा करने पर:$9x - 15y = 12$ --- (3)समीकरण (2) में से (3) को घटाने पर:$(9x - 2y) - (9x - 15y) = 7 - 12\] *** Error message: Display math should end with $$. leading text: \[y$ Unicode character क (U+0915) leading text: \[y$ क Unicode character ा (U+093E) leading text: \[y$ का Unicode character म (U+092E) leading text: \[y$ का म Unicode character ा (U+093E) leading text: \[y$ का मा Unicode character न (U+0928) leading text: \[y$ का मान Unicode character म (U+092E) leading text: \[y$ का मान $x = 1 + y$ म Unicode character े (U+0947) leading text: \[y$ का मान $x = 1 + y$ मे Unicode character ं (U+0902) leading text: \[y$ का मान $x = 1 + y$ में Unicode character र (U+0930) leading text: ... का मान $x = 1 + y$ में र Unicode character ख (U+0916) leading text: ...ा मान $x = 1 + y$ में रख </pre>13y = -5 \implies \mathbf{y = -5/13}<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2571202e5f66a9c7a56e6cb8e0897d80_l3.png" height="45" width="355" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[y$ का मान (1) में रखने पर:$3x - 5(-5/13) = 4 \implies 3x + 25/13 = 4\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>3x = 4 - 25/13 = (52-25)/13 = 27/13<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3a7522a2aa3d83fb202049451034ccd2_l3.png" height="84" width="582" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[x = (27/13) / 3 \implies \mathbf{x = 9/13}$</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --> <!-- wp:list-item --> <li>(b) प्रतिस्थापन विधि (Substitution):समीकरण (2) से: $9x = 2y + 7 \implies x = (2y + 7)/9$इसे (1) में रखने पर: $3\left(\frac{2y + 7}{9}\right) - 5y = 4\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>\frac{2y + 7}{3} - 5y = 4 *** Error message: Missing $ inserted. leading text: ...latex.com-efed48720b2563045cb9ed771ce734b9_ Bad math environment delimiter. leading text: ... class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[ Missing \endgroup inserted. leading text: ...played-equation " alt="\[3 + 3y + 4y = 10\] \begin{document} ended by \end{equation*}. leading text: ...played-equation " alt="\[3 + 3y + 4y = 10\] Missing $ inserted. leading text: ...played-equation " alt="\[3 + 3y + 4y = 10\] Extra \endgroup. leading text: ...played-equation " alt="\[3 + 3y + 4y = 10\] Missing $ inserted. leading text: ...endered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>7y = 7 \implies Bad math environment delimiter. leading text: \[ Missing \endgroup inserted. leading text: \[y$ Unicode character क (U+0915) leading text: \[y$ क3 से गुणा करने पर:
का मान![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com (2y + 7) - 15y = 12<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e076aad6c1b22939a50d4ab84f21d5ee_l3.png" height="19" width="208" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[-13y = 5 \implies \mathbf{y = -5/13}\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>y](https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a65321bf39b2c4d947802470f7574640_l3.png)
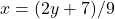 में रखने पर:
में रखने पर: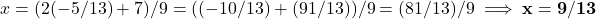
- हल:
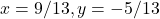
- कौन-सी विधि अधिक उपयुक्त है? विलोपन विधि (
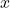 के गुणांकों को बराबर करना) यहाँ कम भ्रामक (less confusing) है।
के गुणांकों को बराबर करना) यहाँ कम भ्रामक (less confusing) है।
(iv) 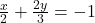 और
और 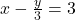
पहले समीकरणों को सरल करें (LCM से गुणा करके):
(1) को 6 से गुणा करें: ![]() — (1a)
— (1a)
(2) को 3 से गुणा करें: ![]() — (2a)
— (2a)
- (a) विलोपन विधि (Elimination):समीकरण (1a) में से (2a) को घटाने पर (क्योंकि
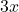 समान है):
समान है):
का मान (2a) में रखने पर:![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com (3x + 4y) - (3x - y) = -6 - 9<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f17d0c0fededab9b03af78f476da1cca_l3.png" height="17" width="180" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[5y = -15 \implies \mathbf{y = -3}\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>y](https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-28ef67ae921e72decd6b0a0d831c9edd_l3.png)
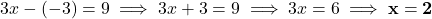
- (b) प्रतिस्थापन विधि (Substitution):समीकरण (2a) से:
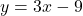 इसे (1a) में रखने पर:
इसे (1a) में रखने पर: *** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula: 3x + 4(3x - 9) = -6<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8ae356060437a1305fde16529fbbbd32_l3.png" height="14" width="154" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[3x + 12x - 36 = -6\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>15x = 30 \implies \mathbf{x = 2}<pre class="ql-errors">*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula: \[x$ का मान $y = 3x - 9$ में रखने पर:$y = 3(2) - 9 = 6 - 9 \implies \mathbf{y = -3}$</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --> <!-- wp:list-item --> <li><strong>हल:</strong> $x = 2, y = -3$</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --> <!-- wp:list-item --> <li><strong>कौन-सी विधि अधिक उपयुक्त है?</strong> समीकरणों को सरल करने के बाद, दोनों विधियाँ बहुत आसान हैं।</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --></ul> <!-- /wp:list --> <!-- wp:separator --> <hr class="wp-block-separator has-alpha-channel-opacity"/> <!-- /wp:separator --> <!-- wp:heading {"level":3} --> <h3 class="wp-block-heading">2. निम्न समस्याओं में रैखिक समीकरणों के युग्म बनाइए और उनके हल (यदि उनका अस्तित्व हो) विलोपन विधि से ज्ञात कीजिए:</h3> <!-- /wp:heading --> <!-- wp:heading {"level":4} --> <h4 class="wp-block-heading">(i) भिन्न (Fraction) की समस्या</h4> <!-- /wp:heading --> <!-- wp:list --> <ul class="wp-block-list"><!-- wp:list-item --> <li>समीकरण बनाना:माना भिन्न = $x/y$ (अंश $x$, हर $y$)शर्त 1: $\frac{x+1}{y-1} = 1 \implies x + 1 = y - 1 \implies \mathbf{x - y = -2}$ --- (1)शर्त 2: $\frac{x}{y+1} = \frac{1}{2} \implies 2x = y + 1 \implies \mathbf{2x - y = 1}$ --- (2)</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --> <!-- wp:list-item --> <li>हल (विलोपन विधि):समीकरण (2) में से (1) को घटाने पर:$(2x - y) - (x - y) = 1 - (-2)\] *** Error message: Display math should end with $$. leading text: \[x$ Unicode character क (U+0915) leading text: \[x$ क Unicode character ा (U+093E) leading text: \[x$ का Unicode character म (U+092E) leading text: \[x$ का म Unicode character ा (U+093E) leading text: \[x$ का मा Unicode character न (U+0928) leading text: \[x$ का मान Unicode character म (U+092E) leading text: \[x$ का मान $y = 3x - 9$ म Unicode character े (U+0947) leading text: \[x$ का मान $y = 3x - 9$ मे Unicode character ं (U+0902) leading text: \[x$ का मान $y = 3x - 9$ में Unicode character र (U+0930) leading text: ...का मान $y = 3x - 9$ में र Unicode character ख (U+0916) leading text: ...ा मान $y = 3x - 9$ में रख </pre>x = 3<pre class="ql-errors">*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula: \[x$ का मान (1) में रखने पर:$3 - y = -2 \implies 5 = y$</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --> <!-- wp:list-item --> <li><strong>उत्तर:</strong> वह भिन्न <strong>3/5</strong> है।</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --></ul> <!-- /wp:list --> <!-- wp:separator --> <hr class="wp-block-separator has-alpha-channel-opacity"/> <!-- /wp:separator --> <!-- wp:heading {"level":4} --> <h4 class="wp-block-heading">(ii) नूरी और सोनू की आयु</h4> <!-- /wp:heading --> <!-- wp:list --> <ul class="wp-block-list"><!-- wp:list-item --> <li>समीकरण बनाना:माना नूरी की वर्तमान आयु = $x$माना सोनू की वर्तमान आयु = $y$शर्त 1 (पाँच वर्ष पूर्व): $(x - 5) = 3(y - 5) \implies x - 5 = 3y - 15 \implies \mathbf{x - 3y = -10}$ --- (1)शर्त 2 (दस वर्ष पश्चात्): $(x + 10) = 2(y + 10) \implies x + 10 = 2y + 20 \implies \mathbf{x - 2y = 10}$ --- (2)</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --> <!-- wp:list-item --> <li>हल (विलोपन विधि):समीकरण (2) में से (1) को घटाने पर:$(x - 2y) - (x - 3y) = 10 - (-10)\] *** Error message: Display math should end with $$. leading text: \[x$ Unicode character क (U+0915) leading text: \[x$ क Unicode character ा (U+093E) leading text: \[x$ का Unicode character म (U+092E) leading text: \[x$ का म Unicode character ा (U+093E) leading text: \[x$ का मा Unicode character न (U+0928) leading text: \[x$ का मान Unicode character म (U+092E) leading text: \[x$ का मान (1) म Unicode character े (U+0947) leading text: \[x$ का मान (1) मे Unicode character ं (U+0902) leading text: \[x$ का मान (1) में Unicode character र (U+0930) leading text: \[x$ का मान (1) में र Unicode character ख (U+0916) leading text: \[x$ का मान (1) में रख </pre>y = 20<pre class="ql-errors">*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula: \[y$ का मान (2) में रखने पर:$x - 2(20) = 10 \implies x - 40 = 10 \implies x = 50$</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --> <!-- wp:list-item --> <li><strong>उत्तर:</strong> नूरी की आयु <strong>50 वर्ष</strong> और सोनू की आयु <strong>20 वर्ष</strong> है।</li> <!-- /wp:list-item --></ul> <!-- /wp:list --> <!-- wp:separator --> <hr class="wp-block-separator has-alpha-channel-opacity"/> <!-- /wp:separator --> <!-- wp:heading {"level":4} --> <h4 class="wp-block-heading">(iii) दो अंकों की संख्या</h4> <!-- /wp:heading --> <!-- wp:list --> <ul class="wp-block-list"><!-- wp:list-item --> <li>समीकरण बनाना:माना दहाई का अंक = $x$, इकाई का अंक = $y$तो, संख्या = $10x + y$अंकों को पलटने से बनी संख्या = $10y + x$शर्त 1: $\mathbf{x + y = 9}$ --- (1)शर्त 2: $9 \times (\text{संख्या}) = 2 \times (\text{पलटी संख्या})\] *** Error message: Display math should end with $$. leading text: \[y$ Unicode character क (U+0915) leading text: \[y$ क Unicode character ा (U+093E) leading text: \[y$ का Unicode character म (U+092E) leading text: \[y$ का म Unicode character ा (U+093E) leading text: \[y$ का मा Unicode character न (U+0928) leading text: \[y$ का मान Unicode character म (U+092E) leading text: \[y$ का मान (2) म Unicode character े (U+0947) leading text: \[y$ का मान (2) मे Unicode character ं (U+0902) leading text: \[y$ का मान (2) में Unicode character र (U+0930) leading text: \[y$ का मान (2) में र Unicode character ख (U+0916) leading text: \[y$ का मान (2) में रख </pre>9(10x + y) = 2(10y + x)<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7599003289bf8488c21c353e3e207947_l3.png" height="16" width="159" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[90x + 9y = 20y + 2x\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>88x - 11y = 0 *** Error message: Missing $ inserted. leading text: ...latex.com-8ae356060437a1305fde16529fbbbd32_ Bad math environment delimiter. leading text: ... class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[ Missing \endgroup inserted. leading text: ...ayed-equation " alt="\[3x + 12x - 36 = -6\] \begin{document} ended by \end{equation*}. leading text: ...ayed-equation " alt="\[3x + 12x - 36 = -6\] Missing $ inserted. leading text: ...ayed-equation " alt="\[3x + 12x - 36 = -6\] Extra \endgroup. leading text: ...ayed-equation " alt="\[3x + 12x - 36 = -6\] Missing $ inserted. leading text: ...dered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>15x = 30 \implies Bad math environment delimiter. leading text: \[ Missing \endgroup inserted. leading text: \[x$ Unicode character क (U+0915) leading text: \[x$ क(11 से भाग देने पर)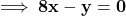 — (2)
— (2) - हल (विलोपन विधि):समीकरण (1) और (2) को जोड़ने पर:
का मान (1) में रखने पर:![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com (x + y) + (8x - y) = 9 + 0<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9207ddeac683e4b353844574f7f2c9bb_l3.png" height="13" width="141" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[9x = 9 \implies x = 1\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>x](https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-21d7bbe193cf6c4e7e2d5a9ae48f4201_l3.png)
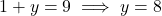
- उत्तर: वह संख्या 18 है।
(iv) मीना के बैंक नोट
- समीकरण बनाना:माना ₹ 50 के नोटों की संख्या =
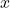 माना ₹ 100 के नोटों की संख्या =
माना ₹ 100 के नोटों की संख्या = 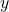 शर्त 1 (कुल नोट):
शर्त 1 (कुल नोट): 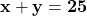 — (1)शर्त 2 (कुल मूल्य):
— (1)शर्त 2 (कुल मूल्य): 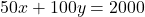 (50 से भाग देने पर)
(50 से भाग देने पर) 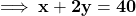 — (2)
— (2) - हल (विलोपन विधि):समीकरण (2) में से (1) को घटाने पर:
का मान (1) में रखने पर:![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com (x + 2y) - (x + y) = 40 - 25<span class="ql-right-eqno"> </span><span class="ql-left-eqno"> </span><img src="https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-cbbfb2f76ba69e9e8c1dda6a884a6f6f_l3.png" height="17" width="50" class="ql-img-displayed-equation " alt="\[y = 15\]" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com"/>y](https://mpeducator.co.in/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a5b83f8891b2529eb78f04f91b6e796c_l3.png)
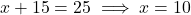
- उत्तर: मीना ने ₹ 50 के 10 नोट और ₹ 100 के 15 नोट प्राप्त किए।